Classification and Marking
Classification and marking are
the processes of identifying the priority of each packet. This is the first
step of QOS control and should be done near the source
hosts. Classification is the process of identifying and categorising
traffic into classes, typically based upon incoming interface IP
precedence, DSCP Source or Destination
address. Application classification is the most fundamental QOS
building block. Without classification, all packets are treated the same.
Marking
Marking is the QOS feature
component that colours a packet so it can be identified and distinguished from
other packets in QOS treatment. Commonly used markers:
link-layer: COS
(ISL, 802.1q), MPLS EXP bits, frame relay
network layer: DSCP, IP
precedence
Layer 2 and Layer 3 Header
Marking
Let's take
a look at the Layer 3 IPv4 packet ToS Byte.
In the beginning, the ToS byte is
defined like this ☝.
- The starting 3 bits are used to define IP precedence. The higher
the value means the higher the priority of IP Packets.
- The rest of the bits are called the Type of Service. ToS bits are
used to assign delay, throughput, and reliability.
Let's see the picture for better
understanding.
But the “type of service” bits, which are a specified delay, throughput, and reliability, have never really
been used. Only the IP precedence bits are used to assign a priority to the IP
packets. Do not be confused by the name Tos 0-7 is called ToS byte, and 4-7 bits is
called ToS bits (Type of Service). Look at the picture below👇. However,
ToS bits (Type of Service) have never been used; only the IP Precedence is in
use for prioritising the IP packets.
Let's talk about what we are actually using nowadays?
The DS
field (Differentiated Services), now we call the ToS byte the DS field,
the name has changed.
DSCP (DiffServ Code Point) provides a 6-bit field for QoS marking in
which the colour code (CS) is also called DSCP value. CS or DSCP 6 bits,
among which 3 bits are the same as IP precedence, and the other 3 bits are ToS
fields. Thus, the DSCP value range is 0 to 63. The graph below shows the DSCP
and IP precedence bits:
DSCP value is also known as
Per-Hop Behaviour PHB is Packets that are marked with a certain codepoint will
receive a certain QoS treatment (for example, queuing, policing,
or shaping). The default Per-Hop Behaviour PHB means that we have a
packet that is marked with a DSCP value of 000000. This packet should be
treated as “best-effort”.
.
Now there are three types of
defined PHBs:
Best-Effort (BE or DSCP 0) is the packet that is marked with a DSCP
value of 000000. This packet should be treated as “best-effort”.
Assured Forwarding (AF) Assured forwarding allows you to provide
assurance of delivery as long as the traffic does not exceed some
subscribed rate.
Expedited Forwarding (EF) is that any traffic class with EF's related DSCP
is given the highest priority
let's see CS, AF, EF, and Best
effort.
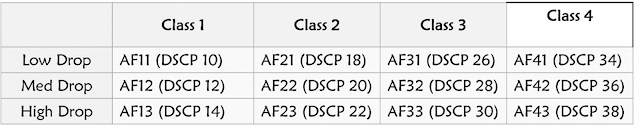
The first bits are called
CS, a higher number means high priority (same as IP Precedence), and the rest
of the 3 bits are called AF higher number means high drop probability assured
forwarding bits.
What are CS and AF?
CS 1 + AF 1 = 001 0100
CS 2 + AF 2 = 010 1000
CS 3 + AF 3 = 011 0110
How does this work?
Let's take an example, we have
FastEthernet 0/0, and the queue is full, and the router wants to drop packets.


Comments
Post a Comment